May 28, 2024
Announcing Rspack 0.7
Rspack v0.7 has been released!
This is the last minor release before the Rspack v1.0. After this, the Rspack team will focus on the development of v1.0 and aim to launch the Rspack v1.0 alpha version soon.
Notable changes in Rspack v0.7:
- Support for Lazy Compilation: Significantly improves the dev startup performance of large applications by compiling on demand.
- Faster CSS Build: Introducing a new css-module-lexer, which increases CSS bundling speed by 4 times.
- Breaking changes: Removed some unstable APIs to make default behaviors more consistent with webpack.
Support for lazy compilation
Rspack v0.7 now supports lazy compilation, which is very helpful for improving the dev startup performance of multi-page applications (MPA) or large single-page applications (SPA).
What is lazy compilation
Lazy compilation is an excellent way to improve startup performance. It compiles modules on demand rather than compiling all modules at startup. This means developers can quickly see the application running when they start the dev server and build the necessary modules in stages.
Why need lazy compilation
Although Rspack itself has good performance, the overall build time can still be less than ideal when building applications with a large number of modules. This is because the modules in the application need to be compiled by various loaders, such as postcss-loader, sass-loader, vue-loader, etc., which introduce additional compilation overhead.
With lazy compilation enabled, Rspack will only compile the entrypoints and dynamic import modules that are requested. This can significantly reduce the number of modules that are compiled at development startup, improving startup time.
Consider the following scenario:
Your team is developing an MPA application with dozens of pages. Most of the time, you only work on a few pages and don't need to build the code for other pages. In this case, you can enable lazy compilation, allowing Rspack to compile only the modules referenced by the pages you access.
When lazy compilation is enabled, Rspack treats "entry points" and "dynamic imports" as split points. For example:
When we compile a.js, Rspack treats b.js as an empty module, as if no code had ever been written to it. As soon as we need to access b.js, Rspack fills the b.js module with its original content, as if the user had just written that piece of code.
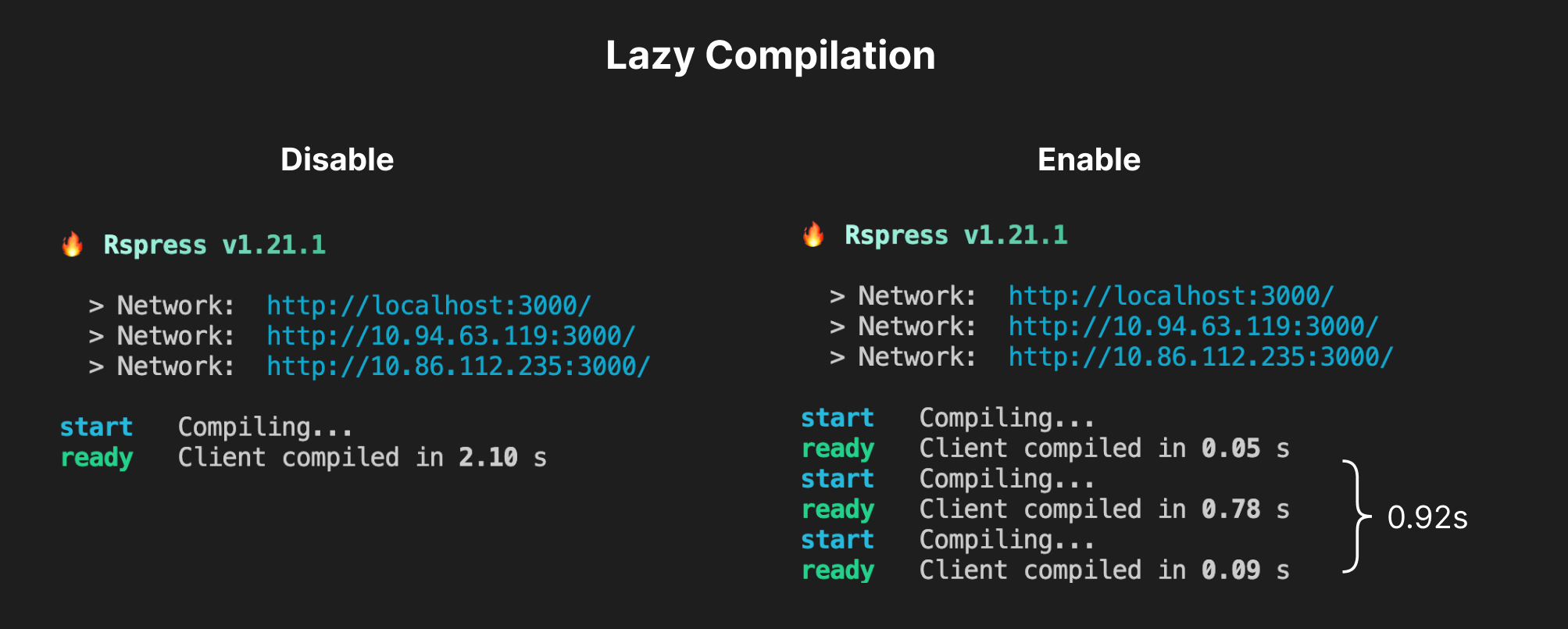
Take the Rspack documentation site as an example, it contains several pages. With lazy compilation is enabled, only the entry points and their dependent modules will be built. This greatly improves startup speed, reducing the startup time from 2.1 seconds to 0.05 seconds.
When a developer accesses a particular page of the site, the build for that page is triggered, and this build time will still be significantly less than the full build time.
How to use
Now, you can enable the lazy compilation feature in Rspack through the experiments.lazyCompilation configuration:
Please note that the current lazy compilation aligns with the webpack implementation, and is still in the experimental stage. In some scenarios, lazy compilation might not work as expected, or the performance improvement may be insignificant.
We will continue to improve the usability of lazy compilation in different scenarios to achieve a more stable state. If you encounter any issues while using it, feel free to provide feedback to us via GitHub Issues.
Faster CSS builds
In v0.7, we have refactored the internal implementation of the experiments.css.
For CSS dependency analysis, we have developed css-module-lexer using Rust. This is a high performance lexer for CSS Modules that can parse CSS or CSS Modules and return their dependency metadata.
With the integration of css-module-lexer, Rspack can now support more complex CSS Modules syntax, making its behaviour align with webpack's css-loader. For example, it can support the following CSS Modules syntax:
The CSS parsing process before and after the refactor is shown in the diagram below:

css-module-lexer has also brought significant performance improvements to Rspack's experiments.css. In performance tests, the building performance of bootstrap.css has increased by about 4x.
- Before refactoring: ~84 ms (analyzing CSS dependencies ~71 ms)
- After refactoring: ~25 ms (analyzing CSS dependencies ~11 ms)
Breaking changes
Rspack will gradually remove all unstable APIs and configurations before version 1.0, and more configurations / APIs / default behaviors will be align with webpack.
Deprecating unstable JavaScript APIs
Rspack early exposed some APIs that were intended for internal use only and were unstable, such as compiler.compilation and compiler.builtinPlugins. These APIs were not stable and could not be used in webpack.
In v0.7, we reorganized the currently exposed APIs and their interface definitions. If you have been using these APIs, you will need to make the necessary adjustments to align with the implementations consistent with webpack.
The following APIs are deprecated:
compiler.builtinPluginscompiler.compilationcompiler.compilationParamscompiler.getAsset(name)statsError.formattedstatsWarning.formatted- ...
For details about the deprecated API, please refer to rspack#6448, rspack#6505.
CSS @import rules must precede all other rules
In Rspack 0.7, we have partially refactored the internal implementation of experiments.css.
After refactoring, when @import is not at the top, you will get the following error. In this case, you need to manually adjust the @import rule to the top.
Remove builtins and experiments.rspackFuture.newTreeshaking
v0.7 has removed the builtins.treeShaking (oldTreeShaking) and experiments.rspackFuture.newTreeshaking (new tree shaking switch) configurations, taking the old tree shaking functionality completely offline.
Remove resolve.browserField
This configuration is shorthand for resolve.aliasFields = ["browser"], and since Rspack already supports resolve.aliasFields, this configuration is no longer necessary.
Remove experiments.newSplitChunks
This configuration is used to enable the new splitChunks implementation, and since Rspack already uses the new splitChunks implementation by default, this configuration is no longer needed.
Remove snapshot
This configuration is used to control the snapshot strategy when using cache. Under Rspack's current incremental rebuild architecture, cache no longer relies on snapshot, so this configuration is no longer needed.
Remove exportsConvention for module type css
This configuration is used to control the naming convention of CSS module exports in experiments.css. It only has an effect on modules with the module type css/module, which have exports. For modules with the module type css, there are no exports, so this configuration is not needed.
Upgrade SWC to 0.91.x
Upgraded the Rust crate swc_core to 0.91.x. This will affect users of the SWC Wasm plugin.
Migration guide
Upgrade the SWC plugins
In version v0.7, the Rust crate swc_core has been upgraded to 0.91.x. Users of the SWC Wasm plugin need to ensure version consistency with swc_core being used, otherwise, it may lead to unforeseen issues.
For more details, please see this document of SWC.
Replace resolve.browserField with resolve.aliasFields
If you previously configured resolve.browserField, you will need to replace it with resolve.aliasFields:
resolve.browserField = trueis replaced withresolve.aliasFields = ["browser"]resolve.browserField = falseis replaced withresolve.aliasFields = []
Remove generator.css.exportsConvention
If you previously configured module.generator.css.exportsConvention or generator.exportsConvention in module.rule, you only need to delete that configuration.
Rsbuild v0.7
Rsbuild v0.7 has been released with Rspack v0.7, please read Announcing Rsbuild v0.7 to learn more.

