March 28, 2025
Announcing Rspack 1.3

Rspack 1.3 has been released!
Notable changes:
- New features
- Performance improvements
- Rstack updates
- Ecosystem
- Upgrade guide
New features
Circular dependency detection
Rspack 1.3 introduces a built-in plugin CircularDependencyRspackPlugin to detect circular dependencies between runtime modules.
This plugin is implemented in Rust and deeply integrated with Rspack's module graph, avoiding expensive data copying and serialization overhead. It detects all circular dependencies by performing a single traversal of the module graph for each entry point, rather than checking each module independently, resulting in lower performance overhead.
Special thanks to @faultyserver for contributing this plugin ❤️
Build HTTP imports
In previous versions, you could import HTTP/HTTPS resources by using externalsPresets.web or externalsPresets.webAsync options, which simply externals the these resources and let the browser (or other platform) to fetch them at runtime.
And the new experiments.buildHttp option provides a new way to import HTTP/HTTPS resources, not fetch the resources at runtime, but download them to the local cache at build time and then bundle them into your output.
See the docs for more details.
Lazy compilation improvements
In previous versions, when lazy compilation was enabled, Rspack would start a separate server to handle lazy compilation-related requests. This led to several issues, such as the need for two servers during development, and the lazy compilation server not being able to share proxy and CORS configurations with the default dev server.
Rspack 1.3 provides new Express-style middleware for integrating lazy compilation that addresses these issues.
- If you are using
@rspack/clior Rsbuild, you can upgrade to the new middleware by simply updating the dependency version. - If you are using a custom development server, you will need to integrate this middleware to support lazy compilation.
Here's an example of how to use the lazy compilation middleware:
AMD supports
Rspack now allows you to enable AMD module support by using the amd option.
Notably, Rspack differs from webpack in that the parsing of AMD modules is disabled by default (webpack enables it by default). This feature is only for compatibility with certain legacy AMD npm dependencies. We recommend prioritizing ES Module dependencies for better Rspack optimization and to boost ES Module adoption.
Add the amd option to enable support:
Special thanks to @nilptr for contributing this plugin ❤️
Performance improvements
Code splitting 25% faster
In Rspack 1.2, we introduced the experiments.parallelCodeSplitting option to enable the new code splitting algorithm.
Starting from Rspack 1.3, this option is enabled by default, resulting in a 25% performance boost for code splitting.
Bundle size optimization
Rspack 1.3 introduces full support for the output.environment option, which allows you to specify which ECMAScript features can be used in the runtime code generated by Rspack, and to generate shorter and more modern runtime code.
By default, Rspack parses the target option and automatically sets the values of the output.environment sub-options based on browserslist to determine which ECMAScript features are supported by the target environment, thus outputting the optimized code.
For example, if Rspack detects that the target environment supports arrow functions, it sets output.environment.arrowFunction to true and using arrow function syntax in the generated code.
By utilizing modern JavaScript features supported by the target environment, Rspack can output smaller runtime code. In our performance testing on a real large-scale project, this optimization reduced the bundle size by approximately 500KB (before gzip compression).
Memory improvements
Rspack now defaults to using mimalloc v3 on macOS. This mitigates some memory consumption issue on macOS during rebuilding. According to some community and internal projects, this would lift the RSS for rebuilding, based on the size of each project, varying from 10% to 85%.
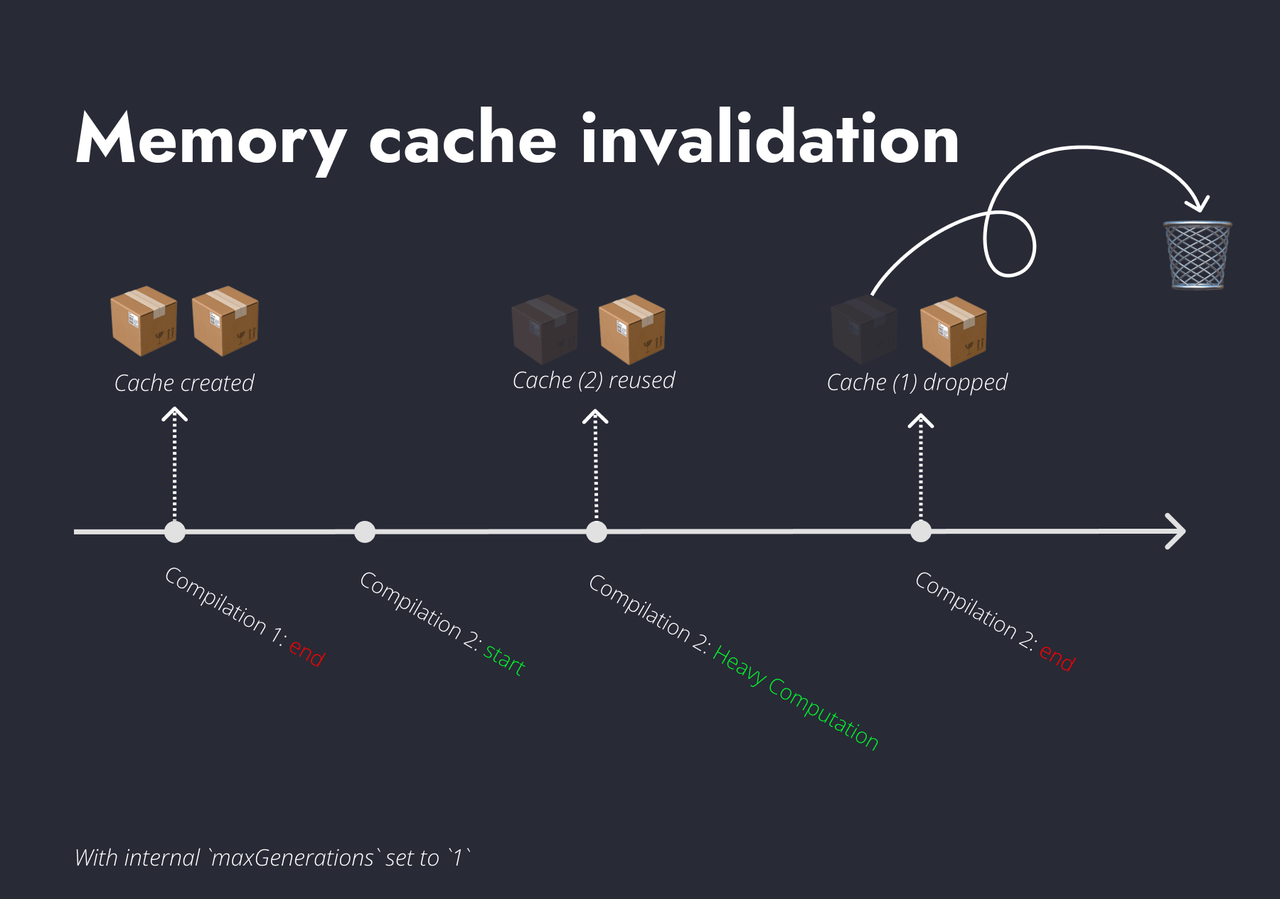
Rspack 1.3 also implemented an internal mechanism to clean the outdated cache: maxGenerations. This controls how many compilations would cache survive if it's not being used by the compiler. Rspack sets the default to 1. This means that the cache will be purged if it's not being used in the next compilation.
Rstack updates
Rsdoctor 1.0
After a year of development and testing, we are proud to introduce Rsdoctor 1.0 — a build analyzer tailored for the Rspack ecosystem and fully compatible with the webpack ecosystem.
Rsdoctor is committed to being a one-stop, intelligent build analyzer that makes the build process transparent, predictable, and optimizable through visualization and smart analysis, helping development teams precisely identify bottlenecks, optimize performance, and improve engineering quality.
Rsdoctor 1.0 introduces significant enhancements:
- A completely redesigned UI that delivers more intuitive and efficient information visualization.
- Rewrote data processing logic using Rust, achieving 20%+ improvement in analysis speed.
- New module search capabilities for analyzing dependencies and module sizes.
Read the Rsdoctor 1.0 release blog for more.
Rsbuild 1.3
Rsbuild 1.3 has been released alongside Rspack 1.3, notable features including:
- Support importing compiled CSS files as strings by using the ?inline query parameter:
- Support importing raw CSS files and static assets as strings by using the ?raw query parameter:
Rslib 0.6
Rslib 0.6 brings the following notable updates:
- Improved CJS output: Rslib's CJS output can now be statically analyzed, allowing Node.js ESM modules to use named imports to reference exports from CJS output.
- Type error optimization: When type errors occur, Rslib now prints the full context and code frame to the terminal, making it easier to fix type issues.
This release also adds support for YAML and TOML. See Rslib 0.6 for more details.
Rspress and Rstest
We are also working on:
- Rspress 2.0: A fully upgraded static site generator with richer features and better performance.
- Rstest: A testing framework powered by Rspack. It delivers comprehensive, first-class support for the Rspack ecosystem, enabling seamless integration into existing Rspack-based projects.
More information will be released soon, stay tuned 🌟
Ecosystem
Rspeedy for Lynx
Lynx is a family of technologies empowering developers to use their existing web skills to create truly native UIs for both mobile and web from a single codebase. Lynx was originally developed by an engineering team of ByteDance, which continues to drive its development.
Lynx has built a modern toolchain called Rspeedy based on Rspack, Rsbuild, and Rsdoctor to enable fast builds. Lynx also features a speedy, versatile rendering engine and performance-driven dual-threaded UI programming.

Read the Introductory Blog of Lynx for more.
Re.Pack 5
Re.Pack is a build tool for building your React Native application.
Re.Pack 5 has been released, which brings unprecedented performance improvements through Rspack, proper microfrontends support through Module Federation 2, simplified configuration and more.
Read the Re.Pack 5 release blog for more.
React Router v7 support
rsbuild-plugin-react-router has been released, which is an Rsbuild plugin that provides seamless integration with React Router v7, supporting the following features:
- Filesystem routes
- Server-side rendering
- Experimental Module Federation support
See rsbuild-plugin-react-router repository to try it out.
Upgrade guide
Module types changed
The module types exported by Rspack have been refined with more accurate type definitions, which helps to align with webpack. Currently supported module subtypes include:
- NormalModule
- ContextModule
- ExternalModule
- ConcatenatedModule
You can now identify a module's specific type in two ways:
The new type definitions may cause type errors in existing JavaScript API code, such as:
To access the resource property, you now need to assert the module type using one of the following methods:
Upgrade SWC plugins
In Rspack 1.3, the Rust crate swc_core has been upgraded to v16. Users of the SWC Wasm plugin need to ensure version consistency with swc_core being used, otherwise, it may lead to unforeseen issues.
For more details, see FAQ - SWC plugin version mismatch.

